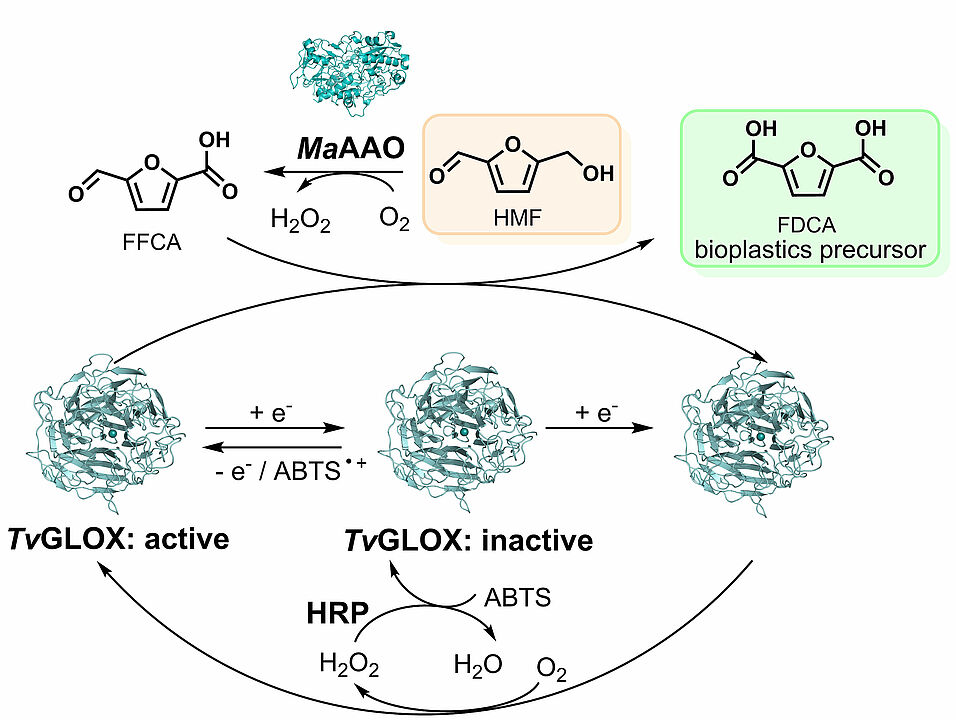
Glyoxal oxidases are promising biocatalysts for the environmentally friendly synthesis of the bioplastics precursor 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid (FDCA), however, they are isolated in inactive form and require activation by oxidizing agents. During her research stay at our institute, Saadet Alpdağtaş from the department of biology, Van Yuzuncu Yil University, heterologously expressed a new glyoxal oxidase from Trametes versicolor (TvGLOX) at high levels in Pichia pastoris and identified a suitable redox activator for continuous reactivation of TvGLOX in conversion of 5-hydroxymethlyfurfural to FDCA in a two-enzyme system. The publication recently appeared in Scientific Reports. Below you can read the abstract. The link to the whole publication can be found in the reference at the bottom.
"Glyoxal oxidases, belonging to the group of copper radical oxidases (CROs), oxidize aldehydes to carboxylic acids, while reducing O2 to H2O2. Their activity on furan derivatives like 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) makes these enzymes promising biocatalysts for the environmentally friendly synthesis of the bioplastics precursor 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid (FDCA). However, glyoxal oxidases suffer from inactivation, which requires the identification of suitable redox activators for efficient substrate conversion. Furthermore, only a few glyoxal oxidases have been expressed and characterized so far. Here, we report on a new glyoxal oxidase from Trametes versicolor (TvGLOX) that was expressed at high levels in Pichia pastoris (reclassified as Komagataella phaffii). TvGLOX was found to catalyze the oxidation of aldehyde groups in glyoxylic acid, methyl glyoxal, HMF, 2,5-diformylfuran (DFF) and 5-formyl-2-furancarboxylic acid (FFCA), but barely accepted alcohol groups as in 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furancarboxylic acid (HMFCA), preventing formation of FDCA from HMF. Various redox activators were tested for TvGLOX reactivation during catalyzed reactions. Among them, a combination of horseradish peroxidase and its substrate 2,2′-azino-di-(3-ethylbenzthiazoline sulfonic acid) (ABTS) most efficiently reactivated TvGLOX. Through continuous reactivation of TvGLOX in a two-enzyme system employing a recombinant Moesziomyces antarcticus aryl-alcohol oxidase (MaAAO) almost complete conversion of 8 mM HMF to FDCA was achieved within 24 h."
Alpdağtaş S, Jankowski N, Urlacher VB, Koschorreck K, 2024, Identification of redox activators for continuous reactivation of glyoxal oxidase from Trametes versicolor in a two-enzyme reaction cascade, Scientific Reports, 14(1):5932, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-56429-z
© 2024 The Authors. This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.